This week I’m heading out to work with intermediate (grade 4-6) teachers on strategies to assist struggling readers.
We’ll focus on three core skill areas central to the Common Core standards – defining, summarizing and comparing using my guide to 18 Strategies for Struggling Readers. (free PDF file)
Plus I’ll introduce some great websites that they can use with the strategies – the new digital literacy meets the old text literacy.
There are two key elements in each skill area that can help students construct meaning and build background knowledge.
Defining
- Before the formal definition has been introduced, students should be asked to make connections between their prior knowledge and the term.
- After the term has been defined, students need activities to more deeply process the term. The focus should be on descriptions, not definitions
Summarizing
- Students should be asked to make their own judgments about what’s important to them (instead of just repeating the details the teacher highlights).
- Students will be able to more readily summarize, if they are asked to share what they’ve learned with an audience other than the teacher. They need use a text structure to organize their thinking.
Comparing
- Students should develop the comparison, not simply repeat the model that we present to them.
- Student should be asked to share what they learned from the comparison. They need use a text structure to organize their thinking.
I’ve selected some Web 2.0 sites that will enable students to use the strategies in a variety online settings. I’ve picked free sites that have easy learning curves. For example, we will use One Word to negotiate meaning through images, explore summarizing text structures with Five Card Flickr and design comparisons with Wordle and Books nGram Viewer.
Working with words
- Explore word frequency with Wordle
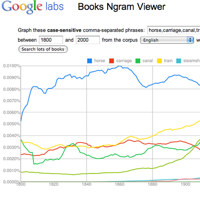
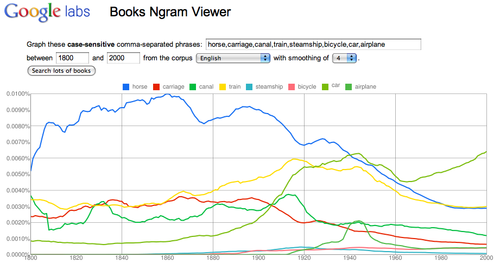
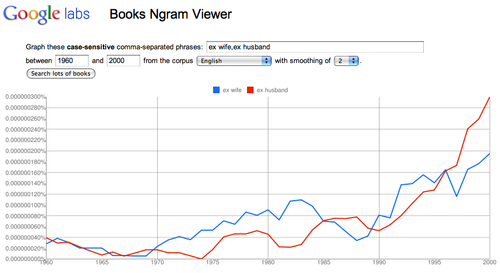
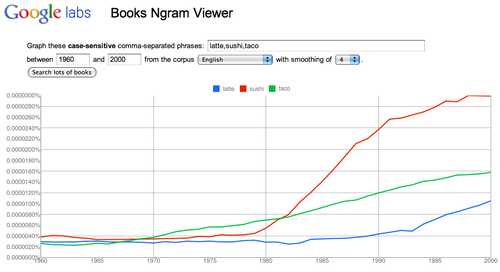
- Search published works with Google Books Ngram Viewer
- Foster writing skills with One Word writing prompts
- Expand vocabulary and word choice with TelescopicText
Working with words and images
- Create mindmaps and graphic organizers with Bubbl.us
- Drag and drop words to create poem based on a photo with Pic-Lits
- Foster visual thinking and creative writing with Five Card Flickr
Kid-friendly search sites
For more ways to use Web 2.0 sites in the classroom
download a free PDF at my post
“87 Free Web 2.0 Projects For the K-12 Classroom“
Image credit flickr/Mike Licht