I frequently conduct large-group workshops for an entire school or district. I use a variety of methods (like audience response systems) to create engaging events that model the practices I am promoting. The workshops resonate well with teachers and I am often asked to come back and “do some more.”
My reply is typically something like, “I’m done talking … it’s time to take this training into the classroom – that’s where the teaching is going on. Besides, you need to build your local capacity.” Over the last 3 years I have developed a classroom walk through (CWT) approach that works. When I return to a school my goal is to serve as a catalyst for dialogue that can be self-sustaining (read – no consultant required).
During my return visit I typically lead groups of teachers on brief CWTs in an effort to try to identify the instructional elements that we addressed in our large-group session. For example, if my large group session was on fostering higher-level thinking skills, then our CWT focuses on trying to see if the CWT visitors can answer the question, “What kinds of thinking did student need to use in the lesson segment we just saw?” If the large group session addressed fostering student engagement, then my walk-through reflection might be “What choice did students (appear to) have in making decisions about the product, process or evaluation of the learning?”
If the large group is “the lecture,” the CWT is the “lab.”
The specifics of CWTs are tailored to the school, but here’s a few of protocols I generally use:
1. CWT groups are kept small – usually only 2 visitors per classroom. (I guide larger groups of teachers, who break into smaller teams to visit classrooms.)
2. Individual CWT visits usually last 10 minutes or less. No note taking or elaborate checklists to fill out. Just watch and listen with a focus on the learning. The real insights occur when we later process our different perspective about what we thought we saw during the CWT.
3. We rotate a pool of subs (or use planning time) to free up teachers for a series CWT sessions that total about 1-2 hours.
4. Teachers are asked in advance if they want to join the CWT and / or be willing to “host” a visit. No “gotchas” or surprises allowed!
5. All teachers are told in advance that we are not doing CWTs to “evaluate them or their lesson.” Our purpose is to use a brief slice of their lesson as a catalyst for a discussion about learning. I ask teachers who did CWTs to get back to the host teachers later in the day to follow up and assure them that our dialogue was about learning, not “their” teaching.
Eleven Reasons Why You Should be Using Classroom Walk Throughs
1. Staff development should look like what you want to foster in the classroom
CWTs can be conducted like roving Socratic seminars – engaging participants in observation, reflection, and discussion. Isn’t that the perspective we want to foster in our students? – thoughtful learners who are reflecting on their progress.
2. CWTs relies on local resources not consultants
Typical PD takes place in the isolation from the students. Herd the teachers into a large lecture hall and let some consultant talk at them. Too often the consultant is viewed as a person with a PowerPoint from somewhere else who wants to sell you the solution to your problem. CWTs can be lead by teachers and move the discussion to the reality of the classroom. More importantly, instead of treating teachers as a passive PD audience they are active participants in staff development.
3. CWTs break through teacher isolation
When I first started teaching 38 years ago, my department chair handed me my class lists and keys and said “Don’t let the kids out ’till the bell rings.” From that day I was on my own and for years I worked in isolation from other adults. Mentoring programs have made great strides with novice teachers since then, but can’t more experienced teachers also benefit from thoughtful discussion and collaboration?
4. CWTs change the dialogue
Let’s face it, our teachers’ lounges are often dominated with complaints about problem students, annoying parents and the unpopular “reform-du jour” from district office. CWT fosters a different discussion. Teacher gain greater respect for their peers. Conversations move in a positive direction – observing, for example, how that problem student behaves in another classroom setting.
5. CWTs clarify your school’s vision of teaching and learning
We spend all this time crafting a school mission (or is it vision?) statement. Let’s see if it holds up in action. Are students given responsibility for their learning, or are they asked to simply follow instructions? If we believe in life-long learning, then how do the educators dialogue to improve our craft?
6. CWTs foster a K-12 conversation
I often lead K-12 teachers on CWTs at different school levels – for example, take high school teachers on a CWT of their feeder elementary and middle school (or vice versa). As one high school teacher said to me as we walked out of a fifth grade classroom, “I didn’t realize what these 5th graders are capable of – I think I need to ‘ramp’ it up a bit at the high school.”
7. CWTs are naturally differentiated
Teachers bring a variety of background knowledge and experiences drawn from different disciplines and grade levels. Our discussion are enriched by their varied perspectives and teachers are free to take away the ideas that resonate with them.
8. We can all learn from each other
During a follow up debriefing, a math teacher remarked to our CWT group that she felt stuck in her approach – it was always foundations first, then have students practice with a series of problems. She asked, “how can you reverse the order and use problems to generate foundation understanding?” The PE teacher replied “when I coach the wrestling team, I put students into a new position and ask them to wrestle their way out of it. In doing so, they discover their own understanding of movement, that I later reinforce with techniques that work from that wrestling position.”
9. It models life-long learning to the students
We ask teachers to explain in advance that teachers will be visiting classroom to improve their skills. As one student once remarked to me, “Still learning to teach? Just kidding – it’s cool to see that you teachers keep working on it!”
10. CWT’s are cost-effective PD
No travel, materials, software, hardware required. With practice, you don’t need the services of an outside consultant. Many of my clients have felt our CWTs were such powerful experiences, that they later continue the CWTs with teachers serving as facilitators.
11. This is PD that is equally valuable for administrators
All my observation about the value of CWTs apply equally well for training administrators. I have led principals (and other admin) on CWTs and found principals to be eager to refocus their thinking away from the traditional evaluation of teachers to more fundamental reflections on the varied dimensions of learning.
If you’ve read this far, you might also like a few other posts:
Lesson Study: Teacher-Led PD That Works
A Guide to Designing Effective Professional Development: Essential Questions for the Successful Staff Developer
The Reflective Teacher: The Taxonomy of Reflection
Like this:
Like Loading...
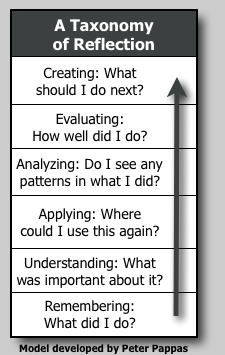



 Recently my post:
Recently my post: 


