This afternoon, I picked up the thread of a LinkedIn discussion “Should we let students opt out of face-to-face education?” Excellent observations by over 100 contributors that got me thinking about what’s next for schools?
That led me back to a post I’d saved on my Evernote by George Siemens who wrote
In education, we have decades of reform rhetoric behind us. I have never heard someone say “the system is working”. There appears to be universal acknowledgement that the system is broken.
Classrooms were a wonderful technological invention. They enabled learning to scale so that education was not only the domain of society’s elites. Classrooms made it (economically) possible to educate all citizens. And it is a model that worked quite well.(Un)fortunately things change. Technological advancement, coupled with rapid growth of information, global connectedness, and new opportunities for people to self-organized without a mediating organization, reveals the fatal flaw of classrooms: slow-developing knowledge can be captured and rendered as curriculum, then be taught, and then be assessed. Things breakdown when knowledge growth is explosive. Rapidly developing knowledge and context requires equally adaptive knowledge institutions. Today’s educational institutions serve a context that no longer exists and its (the institution’s) legacy is restricting innovation.
Digital networks antagonize planned information structures. Planned information structures like textbooks and courses simply can’t adapt quickly enough to incorporate network-speed information development. Instead of being the hub of the learning experiences, books, courses, and classrooms become something more like a node in part of a much broader (often global) network. The shift to networks is transformative in how a society organizes itself (see Wellman’s Little Boxes, Glocalization, and Networked Individualism)
So I followed that link to Barry Wellman who wrote
Members of traditional little-box societies deal principally with fellow members of the few groups to which they belong: at home, in the neighborhood, at work, or in voluntary organizations. …These groups often have boundaries for inclusion and structured, hierarchical, organization: supervisors and employees, parents and children, pastors and churchgoers, organizational executives and members. In such a society, each interaction is in its place: one group at a time.
…Work, community and domesticity have moved from hierarchically arranged, densely knit, bounded groups (“little boxes”) to social networks. … In networked societies, boundaries are more permeable, interactions are with diverse others, linkages switch between multiple networks, and hierarchies are both flatter and more complexly structured. …Rather than fitting into the same group as those around them, each person has her own personal network.
…This is a time for individuals and their networks, and not for groups. The proliferation of computer-supported social networks fosters changes in “network capital”: how people contact, interact, and obtain resources from each other. The broadly -embracing collectivity, nurturing and controlling, has become a fragmented, variegated and personalized social network. Autonomy, opportunity, and uncertainty are the rule.
Complex social networks have always existed, but recent technological developments have afforded their emergence as a dominant form of social organization. Just as computer networks link machines, social networks link people. … The technological development of computer-communications networks and the societal flourish of social networks are now affording the rise of “networked individualism” in a positive feedback loop.
“Should we let students opt out of face-to-face education?” I didn’t see any F2F learning in my brief intellectual journey. It seemed to be a good example of Wellman’s “networked individualism.” Just in time and self-directed – beginning with my LinkedIn network and extending beyond – each hyperlink both a destination and new point of departure. The results - this reflective post which might serve as a catalyst for the readers further exploration of the theme. (I’ll complete this “”positive feedback” loop by adding this post to the LinkedIn discussion.
Why would we shackle our students to a face-to-face education?
~~~~
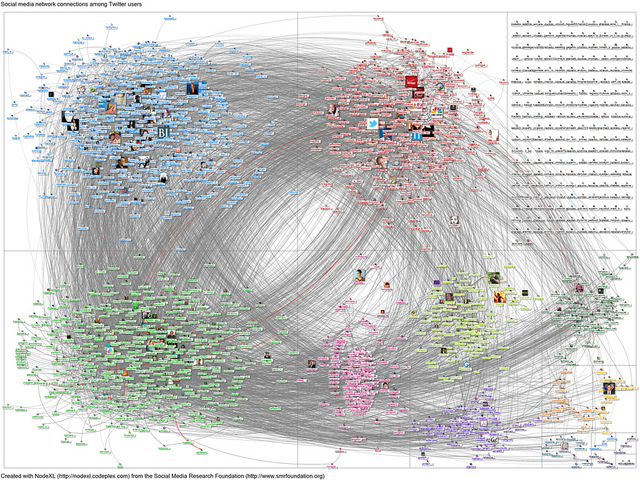
Image credit flickr/Marc_Smith Note: The image shows the connections among the Twitter users who follow the user account @jowyang when queried on December 14, 2011, scaled by numbers of followers (with outliers thresholded). Connections created when users follow one another.