This guest post is written by Greg Wimmer, Central York (PA) High School. I met Greg at TechitU and was impressed by the projects skillful integration of technology and community involvement into the hIstory classroom. Greg’s guest post follows:
As the Advanced Placement exam season draws to an end in early May, I am always left with a month to explore the intricacies of US History with my students. I usually throw a big project at them to occupy their time and push their thinking in ways that I could not have done during the course. This past spring, however, my ideas were lacking and I was fishing for ideas from other faculty members. After speaking with one of our tech assistants, who is also a board member for the York County Heritage Trust, I reached out to Dan Roe, the educational director for the Trust. My goal was to hopefully devise a project we could complete in May. Through our meeting, I learned that the Trust had desired to push their walking tours in to the 21st Century. We explored several options, but decided that the students could write and produce movies for the Trust’s historic walking tours that could be accessed via – Aurasma – a location-based, augmented-reality smartphone app (or a device provided by the Trust). What happened to Aurasma?
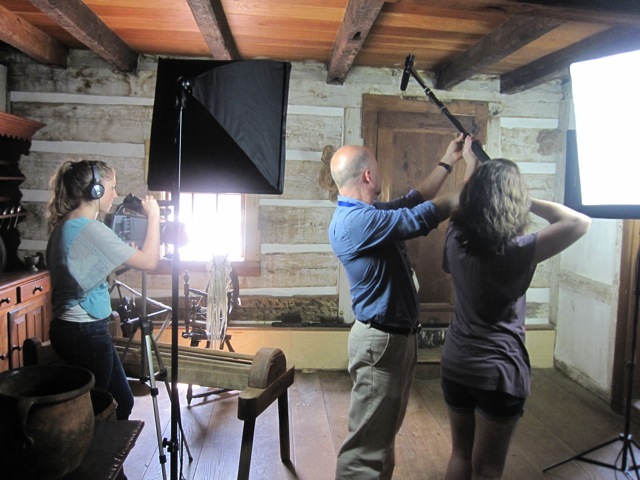
The students were well aware of the project before May, but we unfortunately had no time before then to begin writing the script. In mid-May 2012, Mr. Roe joined my students for two days of collaborative writing. Their scripts focused on two major aspects of York(town) history: 1. York was the political center of the colonies during part of the American Revolution. 2. The Articles of Confederation were completed and signed in York, making it the nation’s first capital. Two groups (of approximately 6 students each) wrote competing scripts for both of the movies. Mr. Roe read the scripts for historical and contextual accuracy and made notes where appropriate. After rewrites were completed, they spent several days writing shot lists and preparing equipment for the shoot. With the exception of a “student on loan” from the TV production class, none of the students had prior experience with equipment or acting.
Students can do amazing things! It’s not until your own students complete a colossal project, that you truly begin to appreciate their capabilities. ~ Greg Wimmer
The first day of shooting took place at the Gates House and Golden Plough Tavern, both built in the mid-Eighteenth Century. Lighting and acting jitters proved to be the biggest hurdles, but we amazingly made it through all of the scenes in about 3 hours. While on set, the students were shocked with amount of detail involved with shooting such a short film. Their respect for film and movie-making increased dramatical over the course of the afternoon.
Filming for day 2 required the students to prep and shoot on the spot with random merchants in Central Market York. Two groups fanned out, asked for participation, and held up cue cards during filming. We also had location shoots scheduled for that afternoon, requiring students to set up and tear down several times. By the end of day 2, the students were exhausted and ready to get back to school.
Making Of Video
They spent the next week tying the project together. Two groups edited the videos separately, one group worked with Aurasma, and the other group prepped for the “making of” video. The groups that edited were shocked with the painstaking process of parcelling the movie together. They ran in to one or two continuity issues while piecing together scenes, requiring creative editing on their part. The two girls who worked on Aurasma ironed out the dilemma of image-based vs. location-based markers. They also took the liberty of creating a YouTube channel for the Heritage Trust as well as other accounts necessary to manage the videos and augmented reality program. The final group helped to create the raw footage for the “making of” video. They devised questions, created a set, and interviewed each of the students in class. They also interviewed Mr. Roe and myself for the video. They spent their final class presenting all of their videos, accounts, and reflections to Mr. Roe. He was thoroughly impressed with their final product and invited future classes to create more content for the Trust.
Lessons Learned:
Jump In – While I am very comfortable with iMovie, I knew little about the movie-making process required to complete “professional” videos. The Trust project gave me the opportunity to learn with the students and collectively tap our creativity. Two years ago, my AP students completed an archaeological dig at an early Nineteenth Century home behind our high school. I worked closely with someone from the Anthropology Department of a local university to organize the event. Going in to the project, I had zero knowledge on the processes involved in such a project. But that’s the point. Showing students that you can (gently) throw caution in to the wind and work together to create something unique and original.
Don’t trust technology and expecting the unexpected – When we returned to the high school at the end of the first day, we needed to download our video from the camera card to make room on the disk for day 2. Much to our surprise, NONE of the video files were there. After much jiggling and encouragement (and 45 minutes later), the computer read the files. I have honestly never watched a file transfer so closely in my life. In that situation, I would not have known how to tell students that their hard work was for nothing. Thankfully, things worked out!
Students can do amazing things! – Like many teachers, I spend a good deal of time looking at blog posts and twitter links to projects created by other classes. It is not until your own students complete a colossal project, that you truly begin to understand the their capabilities. At the same time, the students were giddy about their final product and recognized that teamwork in an academic setting makes for positive results.
Greg Wimmer is the Social Studies Department Chair at Central York High School. He’s in his 10th year of teaching – AP US History and Honors Global Studies. He describes himself as “a husband, father, teacher, and collaborator, I commit myself personally and professional to producing creative avenues for growth. Over the past 9 years, I have searched for new ways to build student understanding through collaboration and ingenuity.” Greg can be reached via Twitter@gregwim
Photo credits: Greg Wimmer