I’ve spent the last month creating my first iBook – “Why We Fight: WWII and the Art of Public Persuasion.” It’s in the “approval” process at the iBookstore. (Look for a post when it’s available).
I learned a lot about making multi-touch iBooks the hard way – trial and error. I thought I’d share a few tips for using iBooks Author (IBA). This post is not an IBA step-by-step. It assumes you are already a bit familiar with IBA. Note: I have collected IBA how-to’s at this Scoop-It.
Carefully plan your pages
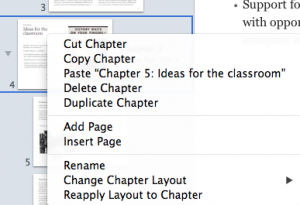
Here’s one big lesson I learned in IBA - you can’t move pages. Chapters and sections of chapters can be easily re-arranged in an iBook. Just highlight them and slide to new location. You can also right click a chapter or section and cut, copy, duplicate and paste. You can even use those commands to move them between two different IBA projects that you have open. BUT moving pages is not allowed. I should note that my book had very little text and loads of graphics and widgets. So, for example, if I wanted my current page 10 to become page 5, I had to recreate pages 6-9 as part of the process. Lesson learned – plan ahead! (This is not a problem if you have a largely text oriented iBook. You could easily cut the text from page 10 and insert it into into a place in the flowing text that would put it at page 5.)
Size matters
File size that is. I planned a multimedia-rich look at the US propaganda effort in WWII. Lots of videos, audios and poster art meant that my iBook file was quickly becoming too large. I used video files from Archive.org that that were in mp4 format. IBA only accepts m4v format and it’s very picky about the types of m4v it accepts. I tried converting mp4 files using Handbrake (a very popular free app). IBA wouldn’t accept Handbrake converted m4v files. I used QuickTime player to convert by opening the mp4 and using QT File / export, but for some reason QT greatly increases file size when exporting.
My final solution to growing file size was three fold. One – I invested in Apple Compressor to convert mp4 to m4v and compress file size. Two – I used iMovie to edit some to the movies to tighten them up. Three – My planned iBook eventually got split into 3 iBooks of smaller file size. One other solution you could use would be to not put the video file in the iBook, but to link to it on YouTube via an embedded widget. (You can easily create a widget for that at a free site – Class Widgets).
Who wrote my iBook?
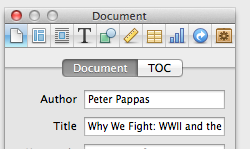
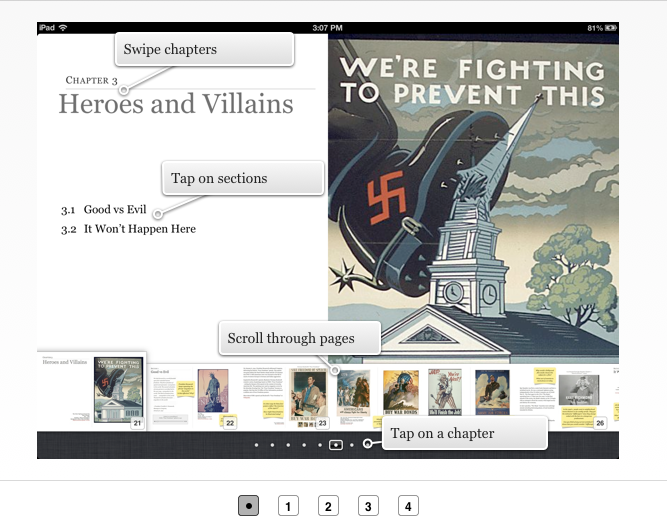
IBA allows you to preview your iBook by connecting an iPad and choosing File / Preview. It gives you the choice to either preview the entire book on your iPad or just preview the section you are working on. For the longest time, when I previewed my iBook it would appear on my iPad as “Author Unknown.” Finally, I figured out I needed to set the title and author in the “Document” section of the Inspector. Lesson learned.
Stylin’

I decided to use frequent stop and think prompts in the book to focus students on reflection. It was also away to reinforce CCSS skills throughout the book in a user friendly manner. I created a yellow post-it style text box and liked the way it looked. One I had the format I wanted I was able to copy and paste using the tool bar icons. BTW - You can also edit / copy and edit / paste widgets. A nice way to move them around.
Don’t mess with chapter image placeholders
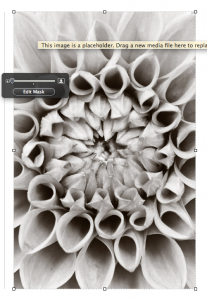
My iBook was loaded with media content, so I used the “Basic” template offered by IBA. One of the first things I did was strip it down to blank white pages. My mistake was revealed when I looked at my iBook in the “Table of Contents” view. I noticed that my chapter start pages lacked the graphics I had put on them. I finally figured it out.
When you create a new chapter you are offered an image place holder on the right side of the page. Don’t delete it like I did. Instead, just drag your image into it. That way the image will appear in the ”Table of Contents” view. Once I deleted the image placeholders there was no way to get them back. You guessed it – I needed to create a “new chapter” and rebuild all the content. Ouch!
Customize layout for your widgets
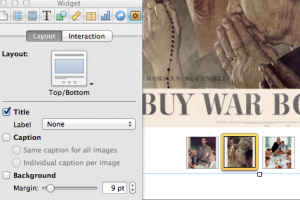
I was going for a very clean minimal look that would showcase the content. So I wanted my widgets to have minimal styling.
To do that - go to Widget in the Inspector panel. Choose “Layout” tab and deselect background. Lots of other options for Label and Caption. You can also show thumbnails (as I did on the left) by selecting them in the “Interaction” tab.
Sneaking up on hyperlinks and bookmarks
You can hyperlink from the iBook to external links or create Bookmarks to jump between content within your iBook. Use the Inspector to create them. Here’s a few tips. You can only hyperlink from text. No image hyperlinks. You can hyperlink from any body text or text within inserted text boxes to URLs outside your iBook. Be sure to copy / paste you new URL into the Inspector or you’ll be creating a hyperlink to Apple.
Bookmarks are a bit fussier. First you need to turn some text in your iBook into a bookmark using the Inspector - select the text and click on the + sign to add new bookmark. Here’s the catch – you can only create a bookmark from body text – you cannot bookmark text in a text box. Once you have anchored a bookmark you select some other text in your iBook and use Inspector to hyperlink to your bookmark.
Working with hyperlinks after you create them is a bit quirky. If you click on a previously created hyperlink in your iBook, it work. In other words you’ll leave the iBook and go to the URL in Safari. So you have to “sneak up” on hyperlinks. Click your cursor into adjacent text and use your keyboard arrows to navigate into the hyperlinked text. It will go active and you can use the Inspector to make changes.
Where’s the Find and Replace?
IBA has a some good editing tools. You can use Edit / Proofreading to get to a reasonable proofreading panel. I found it useful. Looking for the find and replace feature? Use keyboard Command – F.
Like this:
Like Loading...