I’ve long held that staff development should model what you want to see in the classroom, and for that reason I wouldn’t do a workshop without using a student response system. (SRS)
I’ve long held that staff development should model what you want to see in the classroom, and for that reason I wouldn’t do a workshop without using a student response system. (SRS)
I’m not interested in using a SRS to pose objective questions or host a “game-show” style workshop. I see a SRS as a discussion catalyst and a tool to model instructional strategies. For example, I can ask a Likert scale question, post the audience results, and ask them “Does anyone see any patterns in the data?” I get responses and discussion that I never got in my pre-SRS “raise your hand and tell me what you think” days. Likewise, I can easily model a problem-based approach and give teachers first-hand experience in what that type of learning “feels” like to a student.
My favorite “clicker-based” SRS is TurningTechnologies‘ TurningPoint system. It’s been a central feature of my workshops for many years. But my quest to develop a more highly-interactive webinar PD model led me to investigate “bring your own device” (BYOD) web-based SRS systems. My goal was to offer webinars that rose well above the typical “listen to the presenter’s voice while you look at their PowerPoint” model.
Learning Catalytics kept us engaged more than simply sitting and consuming. You modeled everything you were suggesting we try.
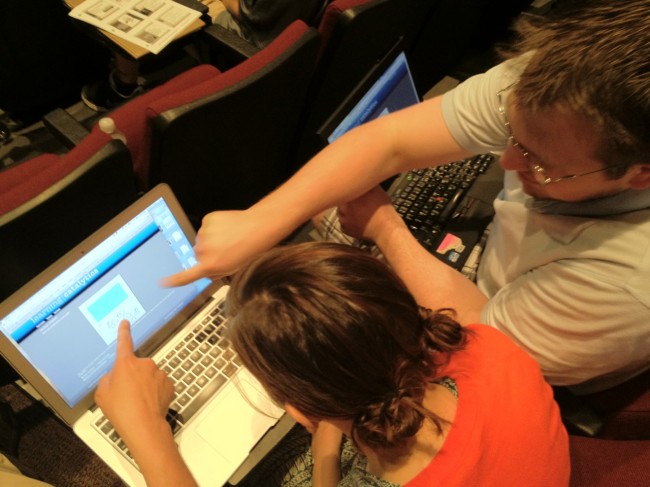
Thus I found Learning Catalytics – a powerful BYOD-SRS system. After getting great reviews in my webinars, I thought I’d give Learning Catalytics a try with a live audience of about 100 secondary teachers at a recent workshop I gave at the Mary Institute and Saint Louis Country Day School (MICDS) in St Louis. (I’m still using TurningPoint clickers. I bought along a set to use in a separate session with about 50 MICDS elementary teachers.)
I thought I share some observation from my experience with Learning Catalytics to encourage other educators to give it a try. Learning Catalytics is currently running a free 30-day trial for use with up to 100 students.
Learning Catalytics is a web-based system that allows the teacher to create a wide variety of open-ended responses beyond the usual multiple-choice, priority, and ranking. Creating new questions is easy and the system allows for copy / paste of text – it even lets you use that function to paste in multiple responses to a question in one action. There’s also a growing (and searchable) library of questions to draw from. Teachers deliver questions and manage the presentation via the web from their laptop (or tablet).
… appreciated the modeling of Learning Catalytics – great examples of how to use it across different disciplines. ..the idea of placing us in our students’ shoes – which felt very uncomfortable at times – was really useful in the end.
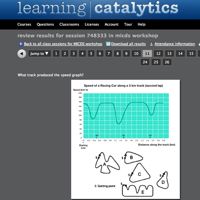
The system has an array of powerful response monitoring and reporting tools, and it’s a stand out at fostering peer discussion. Teachers can easily create a student seat map and use it to quickly see who “gets it.” Learning Catalytics can review student responses and direct them to discuss their answers with nearby peers who may have different views. It even send out a message telling them to talk with specific class members. “Cameron turn to your right and talk to Zoe about your answer.” Questions can be asked multiple times and students can teach their peers before the next re-polling. Collaborative learning is one of the driving principles behind Learning Catalytics.
Students can use any web-based device they already bring to class to answer questions – laptop, tablet, smartphone. You don’t even need to project Learning Catalytics on the presentation screen since all questions (including graphics and results) get pushed out to the student units. (Note: I’m already testing an iPad + Apple TV approach to integrate presentation and SRS in a wireless delivery model.) The system ran flawlessly on the MICDS wifi network. (The internet bandwidth we were pulling during the polling sessions was about 30MB for about 100 participants.)
Our workshop at MICDS explored teacher and student perceptions of “Rigor, Relevance, Reflection: Learning in the Digital Age.” Learning Catalytics’ great variety of question formats spawned some lively group discussion and teacher reflection on those themes.

As a defining exercise I posed the following: “The MICDS mission statement notes that ‘Our School cherishes academic rigor.’ Write 3 words (or phrases) that you associate with academic rigor.
While Learning Catalytics can gather short or long responses as a list, I chose to have it create a “word cloud” out of participant replies – imagine the power of instant “Wordles.” (See resulting word map left)
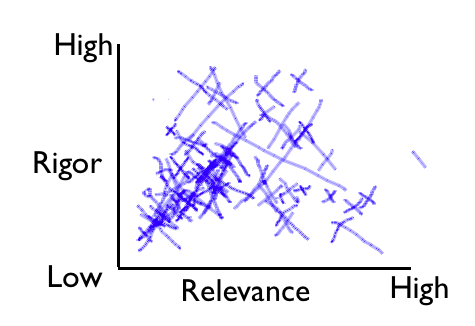
Learning Catalytics provides a “composite sketch” question. Students can use their mouse or touch screen to indicate a point or draw a line on their device. The results are aggregated into a single response by overlaying all the individual responses. To emulate a “classroom walkthrough” I shared a sample lesson and asked teachers to plot their perceptions of its rigor and relevance on an X / Y axis. The resulting overlay graph of the variance in their responses (below) was a powerful discussion starter.
There’s other question formats that add interesting functionality, and teachers can incorporate graphics to create more engaging questions. For example: Students highlight words in a body of text – the frequency results become a “heat map.” Students indicate priority or sequence by promoting or demoting choices – the results show the relative strength of each choice. Students indicate a region on an image by touching or clicking on a point – the results aggregate on a “regional map.” I’m still exploring Learning Catalytics and I give a big hat tip to Brian Lukoff, it’s CEO and co-founder. He’s helped me translate my instructional goals into interesting questions and has been very open to my suggestions for new formats and control panel features.
To round out my post, here’s some MICDS teacher responses to a few of my evaluation prompts:
To what extent did the workshop model effective instructional techniques?
- Finally a presenter who modeled what he preaches.
- It was interactive, engaging, and collaborative.
- Learning Catalytics kept us engaged more than simply sitting and consuming. You modeled everything you were suggesting we try.
- Asking us to be in position of actual learners was a good reminder of what students feel and suggested ways to promote actual learning.
- I thought it was interesting how you tried to manage speaking and teaching 100+ adults with minimizing the lecture format. I was impressed at your use of think/pair/share.
- It provoked my reflection on my teaching, i.e. students take ownership evaluating and sharing.
What, if any, impact will this workshop have on your practice?
- It reassured me that I’m on a good track in terms of relevance and innovation.
- I will look to use more driving question, more peer sharing, and more student choice.
- The workshop makes me seek ways to develop and practice student to student conversation.
- I am going to immediately revamp how I plan to intro the genetics experiment and make it more open ended and student centered
- Reinforced my call for increased relevance to student world and understanding the skills that students need to operate in the digital world.
- I would like to give students more control over their work.
- It has caused me to think about giving students more responsibility for their learning.
Any comments on the Learning Catalytics response system?
- Love the Catalytics…
- I really liked it–very intuitive, very useful in creating class feedback and interaction.
- I liked how the Wordle was embedded in the presentation. It was automatic and quick. I would like to be able to do that in my classes.
- I like the Learning catalytics system as a way to engage everyone, with immediate access to the results. I like the open-ended questions.
- I liked how the technology was used to get our feedback. There was collaboration, discussion and evaluation happening.
- LOVED LC. In love. I wanna use it.
- I particularly appreciated the modeling of Learning Catalytics – some great examples of how to use it across different disciplines. Also, I think that the idea of placing us in our students’ shoes – which felt very uncomfortable at times – was really useful in the end.
- I liked seeing others responses. I always appreciate immediate feedback.
- Love LC!!!!
Like this:
Like Loading...