My Social Studies Methods class at the University of Portland recently published a free multi-touch iBook – Exploring History: Vol II. It features ten engaging questions and historic documents that empower students to be the historian in the classroom. For more info on our project and free download of multi-touch iBook version click here.
To better publicize student work, I’m featuring each chapter in it’s own blog post. More in series here.
Your task is to examine the context of these documents and decide which are most helpful to your understanding of the conflict.
Little Rock Nine: Evaluating Historical Sources by Christy Thomas Download as pdf (8.7MB)
This chapter examines the historic setting of the Little Rock Nine though a variety of documents. They include news photographs of the events, governor’s proclamation, historic essays, Presidential speech, TV news reports and video reflections by participants. Your task is to examine the context of these documents and decide which are most helpful to your understanding of the conflict.
- What do you see as the roots of the conflict?
- What motivated the different players involved?
- Which documents do you learn the most from?
As I approached the DBQ assignment, I decided to use images and texts from a literacy class assignment I had just completed. At first, I thought I had a head start, since I had a collection already curated, but as I continued with the assignment I realized I had started in the wrong place. While it was nice to have images and text, I should have started with the essential question AND what I wanted students to experience as they worked through the DBQ.
Working backwards, one of the challenges is finding the essential question that ties everything together. My previous assignment was over a broad topic – the Civil Rights Movement – which I’ve realized is much too broad for a DBQ exercise. Finding the right essential question was key to finding a way to connect the materials together.
The next step was to really think about what I wanted my students to learn as they worked through the DBQ. My first set of materials were loosely related, but would require students to take some large leaps to find the connections. Even with scaffolding questions, it seemed like a stretch. Once I had an essential question identified, then I could focus on the historical thinking skills I wanted students to experience as they worked through the DBQ.
This experience reminds me that the only way to get better at something new is to continue to practice. I have a much better sense of how to organize my thoughts around creating a DBQ and look forward to adding this learning experience to my curriculum development skills.
~ Christy Thomas AboutMe
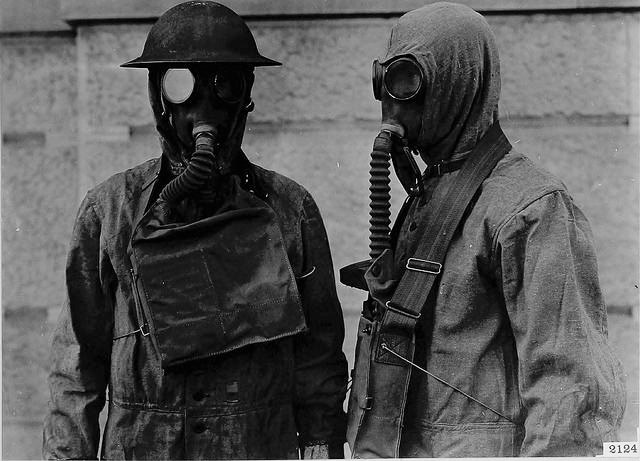
Image Source: Soldiers from the 101st Airborne Division escort African-American students to Central High School in Little Rock in Sept. 1957, after the governor of Arkansas tried to enforce segregation. Photo courtesy National Archives. Operation Arkansas