My last post, What is Writing For?, concluded by offering three ideas for motivating student writers:
- Let students make some choices about their writing.
- Let them write for a more authentic audience than the teacher.
- Use more peer evaluation and self reflection.
We read everything over to see if it made sense to our audience ~ 6th grader’s reflection
I thought readers deserved an example of these principles in action. Here’s a project I did that exemplifies choice, authentic audience and self-reflection.
I worked with a team of 6th grade teachers to demonstrate the power of comparison skills to help their students build vocabulary and content knowledge about the functions of various organs of the human body. (Based on Robert Marzano’s Building Background Knowledge for Academic Achievement and Classroom Instruction That Works). Additionally we wanted to enhance technology skills and demonstrate the power of student choice and self reflection in a PBL setting.
Students are motivated by writing for an authentic audience. “Publishing” helps students master content and develop project management and teamwork skills. The power of publishing enables students to think like writers, to apply their learning strategies and to organize and express their learning. It exemplifies the best of the information revolution – students as creators of content rather than as passive audience.
Project overview:
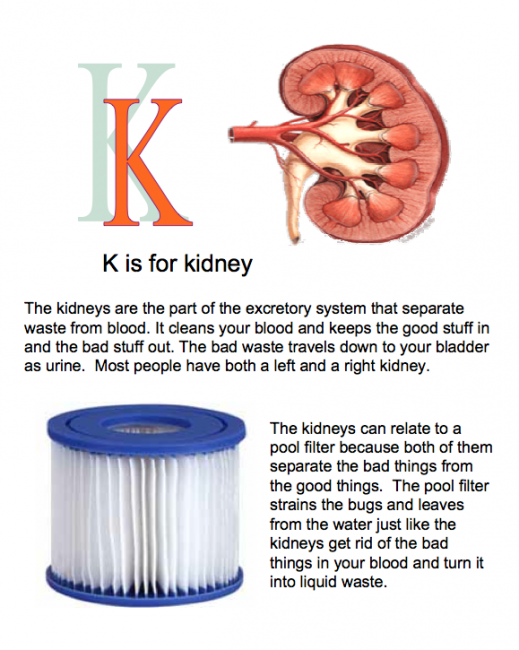
- Students were tasked with developing books to teach the organs of the human body to third graders.They decided that the best idea was an ABC book - ”Traveling Through the Human Body with ABCs”
- Teams of students chose an organ and had to develop a description of function suitable for 3rd grade audience. Then they were asked to compare the organ to something that functioned in the same way and develop a comparison that 3rd graders would understand.
- All the content developed by students went through a peer review process for accuracy and suitability for 3rd grade audience.
- PowerPoint was used to layout graphics and text. Update: you might consider design and publication using iBook Author.
- Students and teacher were guided through a series of reflective prompts.
- The PowerPoints were converted to PDF files and used to publish a few copies of each classes book using Lulu print of demand.
Teacher reflections included:
- Students learn best from doing and from doing it together with support but no interference from adults. Students can explain concepts and ideas to each other in “kid-friendly” language more easily, sometimes, than adults can.
- The lessons are more lasting because they happened in a social context rather than the “top-down” structure of a traditional classroom.
- Project-based learning creates a student centered classroom with the students doing the real work of real learners. The teachers’ work is primarily off-line.
The book is available in print from Lulu as an iBook at iTunes.