Reflection can be a challenging endeavor. It’s not something that’s fostered in school – typically someone else tells you how you’re doing! Teachers are often so caught up in the meeting the demands of the day, that they rarely have the luxury to muse on how things went. Moreover, teaching can be an isolating profession – one that dictates “custodial” time with students over “collaborative” time with peers. In an effort to help schools become more reflective learning environments, I’ve developed this “Taxonomy of Reflection” – modeled on Bloom’s approach. It’s posted in four installments:
1. A Taxonomy of Reflection
2. The Reflective Student
3. The Reflective Teacher
4. The Reflective Principal
See my Prezi Tour of the Taxonomy
3. The Reflective Teacher
Each level of reflection is structured to parallel Bloom’s taxonomy. (See installment 1 for more on the model). Assume that a teacher looked back on an lesson (or project, unit, course, etc) they have just taught. What sample questions might they ask themselves as they move from lower to higher order reflection? (Note: I’m not suggesting that all questions are asked after lesson – feel free to pick a few that work for you.) Remember that each level can be used to support mastery of the new Common Core standards.
taxonomy of reflection
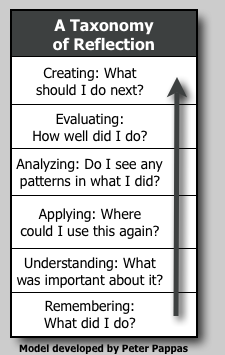
Bloom’s Remembering: What did I do?
Teacher Reflection: What was the lesson? Did it address all the content? Was it completed on time? How did students “score” on the assessment?
Bloom’s Understanding: What was important about what I did? Did I meet my goals?
Teacher Reflection: Can I explain the major components of the lesson? Do I understand how they connect with the previous / next unit of study? Where does this unit fit into the curriculum? What instructional strategies were used? Did I follow best practices and address the standards?
Bloom’s Application: When did I do this before? Where could I use this again?
Teacher Reflection: Did I build on content, product or process from previous lessons? How does this lesson scaffold the learning for the next lesson? How could I adapt the instructional approach to another lesson? How could this lesson be modified for different learners?
Bloom’s Analysis: Do I see any patterns or relationships in what I did?
Teacher Reflection: What background knowledge and skills did I assume students were bringing to the lesson? Were the instructional strategies I used the right ones for this assignment? Do I see any patterns in how I approached the lesson – such as pacing, grouping? Do I see patterns in my teaching style – for example do I comment after every student reply? What were the results of the approach I used – was it effective, or could I have eliminated or reorganized steps?
Bloom’s Evaluation: How well did I do? What worked? What do I need to improve?
Teacher Reflection: What are we learning and is it important? Were my assumptions about student background knowledge and skills accurate? Were any elements of the lesson more effective than other elements? Did some aspects need improvement? Were the needs of all learners met? What levels of mastery did students reach? What have I learned about my strengths and my areas in need of improvement? How am I progressing as a teacher?
Bloom’s Creation: What should I do next? What’s my plan / design?
Teacher Reflection: How would I incorporate the best aspects of this lesson in the future? What changes would I make to correct areas in need of improvement? How can I best use my strengths to improve? What steps should I take or resources should I use to meet my challenges? Is there training or networking that would help me to meet my professional goals? What suggestions do I have for our leadership or my peers to improve our learning environment?
image credit: flickr/duane.schoon



 I first published this post at the start of the 08-09 school year.
I first published this post at the start of the 08-09 school year.