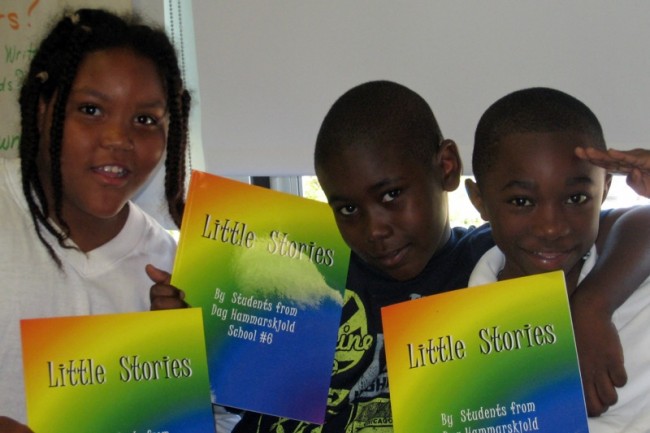
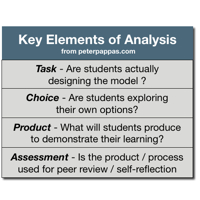
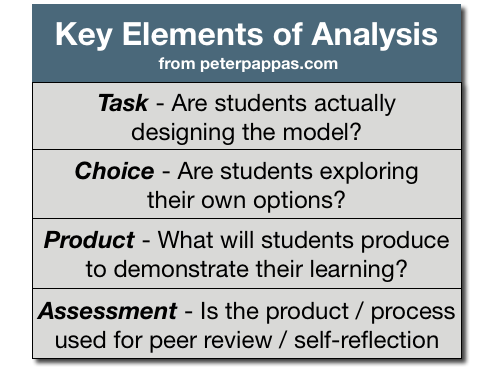
Publishing with PowerPoint is a new book that guides teachers and students through the process of creating and publishing their own books. It’s written by three dear friends and former colleagues – Patricia Martin, MaryAnn McAlpin and Suzanne Meyer. For a few years I had the chance to collaborate with them on some student publishing projects. They’ve continued to hone their skills on broad array of innovative projects. Recently they compiled all they’ve learned into an easy to use guide to using PowerPoint as a book design tool and how to team PPT with the exciting new technology of on-demand printing. Publishing with PowerPoint – available at Amazon
Here’s their guest post detailing the book:
Publishing is an effective tool for getting students engaged and writing. The new book, Publishing with PowerPoint, walks the reader through a process of self-publishing that can be used in any classroom. PowerPoint is an effective book design software – it’s already on your computer and everyone know how to use it. Students find it easy to use PowerPoint templates and position a wide range of text and images on a PPT slide. Powerpoint slides can be quickly grouped and rearranged into book pages. Finally, converting PowerPoint slides into pdfs for publishing can be done with the “Save As” function. Visit Amazon Books / Publishing with PowerPoint to see the use of templates and layouts on the sample pages.
The teacher with a limited budget can print just one copy for the classroom. Parents can order their own copies online.
Publishing with PowerPoint was published through Createspace, an Amazon company, using the process detailed in the book. Once the slides were created, the authors merely converted the slides to PDF’s and sent the result to Createspace. For example, a 32 page, 8.5”X11” color book would cost its authors about $4.00 a copy plus $3.59 shipping and handling. (The shipping and handling costs are calculated at $3.00 per order and $.59 per item). Lulu, another popular on-demand publisher, would price a similar book at $13.42 plus shipping and handling.
The magic of on-demand printing is that the teacher with a limited budget can print just a single copy for the classroom. Both Createspace and Lulu offer options for easy distribution. PTAs or families who want copies can log in and order their own. No need for teachers to take book orders.
The thought of publishing with students might seem daunting - I’ve got too much on my plate as it is! But if you believe in the power of PBL and motivation of writing for an authentic audience, you’ll appreciate this detailed guide book. It offers an overview of the resources necessary for successful publishing. Readers learn how to use PowerPoint’s built-in tools for template design, layout or page design, creating facing pages, and inserting images. The book is organized to walk the reader through the process, detail-by-detail, in the exact order in which the publishing process happens.
The second half of the book is devoted to content. Teachers will realize that content is actually the initial consideration whether looking at writing process or traits of writing. But, it seemed important to the authors that the book present the techniques of publishing (the new information) before reviewing the writing and organization of content for publishing (the prior learning). Using examples from our publishing experiences, the book includes a wide range of samples representing different grade levels, fiction or non-fiction, single-author or anthology that the teachers can use as models.
The book exemplifies the ease with which students can complete the writing process by publishing their work to a wide audience with tools available in a classroom. Hopefully the book will illustrate to its readers the versatility and creativity that PowerPoint can bring to the self-, or on-demand, publishing process. For the teacher who wants to publish electronically the book is an equally invaluable resource to enable students to produce a quality final product. Formatting pages through PowerPoint and creating pdfs work equally well for that application.
Teachers inexperienced with publishing and limited resources do not have to eliminate student publishing options. Publishing with PowerPoint and the use of economical self-publishing can bring this opportunity to any classroom.