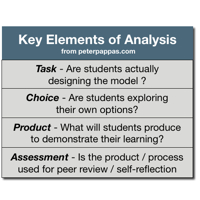
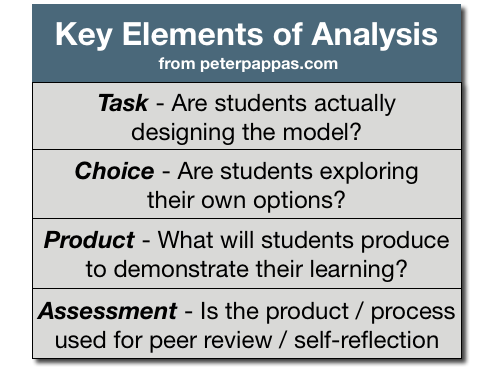
CCSS offers an incentive for teachers to use historic documents to build literacy skills in a content area while empowering students to be the historian in the classroom. But document-based (DBQ) instruction in this context requires four key elements to be successful:
- The right documents.
- Knowing how to look at them.
- Letting students discover their own patterns, then asking students to describe, compare and defend what they found.
- Basing the task on enduring questions, the kind that students might actually want to answer.
My just-published, second iBook – Workers Win the War: Toil and Sacrifice on the US Homefront – embodies that approach. Free at iTunes. It features:
Engaging source material that can be easily interpreted by students. Too often, DBQs use documents that require too much background knowledge to “interpret.” This collection offers over 60 pages of easy-to-intrepret media, much of it visual – including 80 posters, 18 films, cartoons, radio broadcast, recording and sheet music and a dozen rarely-seen pamphlets.
An interactive primary source analysis tool developed by the Library of Congress. Poster and film analysis is modeled in an multi-touch widget. Students can use an iPad-friendly historic document guide to analyze all the source material and share their observations with peers and teachers.
All across the curriculum, students are told to “analyze” material, but their thinking is constrained by the mandated Venn diagram or T-chart. Developing a comparative schema is messy work – but that’s where the learning takes place. To scaffold student analysis, “Workers Win the War” features CCSS-based prompts that ask students to stop and think more deeply about the content.
Essential questions that make an examination of the US homefront in WWII relevant to students’ lives today. Students experience first-hand how the government mobilized public support for the war through higher taxes, hard work and sacrifice.
Contrast that era with our “homefront” experience today, when only our troops and their families have been asked to make sacrifices for wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. Today many see “big government” as an intrusion in their lives. In contrast, during WWII Washington played a very active role shaping American behavior and attitudes in support of hard work and sacrifice in support of the war effort.
Workers Win the War examines the themes of hard work and sacrifice through a variety of perspectives – increasing industrial production, food as weapon, worker health and safety, making do with less, scrap drives, rationing, price controls, and financing the war with higher taxes and bond drives.
Students will enjoy the content: Cartoons featuring Bugs Bunny, Donald Duck and Daffy. Films and posters that equated sick days and long work breaks as near treason. Long-forgotten pamphlets that coached volunteer bond salesmen or advised school principals on how to organize a paper scrap drive – “turn your students into Paper Troopers!” Posters that chided “foolish women” who ignored price ceilings – “Why Shouldn’t I Buy it? I’ve got the Money!”
My favorite is a short film that features two spunky young working women who set out to buy some steak in violation of rationing limits. It turns into a nightmare sequence that demonstrates “rationing means a fair share for all.”
To deepen their understanding of the historic content and hone their Common Core skills, students need a chance to create a unique product to demonstrate their learning. With that goal in mind, Workers Win the War has been designed to leverage the content-production capacity of the iPad.
All of the historic content in the iBook is in the public domain. Each source document is hyperlinked back to archives that provide access to the digital content. Students can easily remix the historic documents into their own galleries and projects.