My Social Studies Methods class at the University of Portland recently published a free multi-touch iBook – Exploring History: Vol II. It features ten engaging questions and historic documents that empower students to be the historian in the classroom. For more info on our project and free download of multi-touch iBook version click here.
To better publicize student work, I’m featuring each chapter in it’s own blog post. More in series here.
First Ladies as a Political Tool by Emily Strocher Download as PDF (5MB)
We do not elect our First Ladies … but we can and do criticize them just as if they were politicians.
Some of the Presidential wives made great First Ladies and some did not, but, overall, the nation has been most fortunate in the caliber and charm of the women who presided at the White House table, stood beside their husbands in innumerable receiving lines and served, each in her own way, in what must be the most trying unpaid fulltime job in the country. We do not elect our First Ladies nor can we turn them out of office but we can and do criticize them just as if they were politicians. (And indeed some of them are!)” ~ Sadler, Christine. “America’s First Ladies,”
As you proceed through this section of the book, answer the multiple choice questions about what category each photograph should be placed in.
- Why did you choose to place the images in the categories that you did?
- What is the importance of these themes? Why would photos that support these ideas be important to have?
- How do you feel these photos illustrate how the First Lady and First Family can be used to spread an idea?
- What do you notice about where the First Lady is standing in each of these photos? Do you think this photograph was staged or candid? If it was staged, why would the individuals in it be posed as they are?
Reflection by Emily Strocher
In addition to being practice in how to go about making a DBQ, this assignment has also been a solid lesson in how not to create a DBQ. I feel that as an actual practicing teacher, this will be easier as I will have a better idea of what I want and need the DBQ to do. I will have a topic in mind, and a message that I am trying to convey to the students, or messages that I want them to come up with on their own. There will be more structure in place. Creating a DBQ in the manner that we did for this class allowed me too much freedom, I feel. I needed a more concrete goal, as my DBQ turned into doing whatever I wanted to with it, not trying to meet specific requirements for student learning.
Going along with that, I decided early on that I wanted to create an image based DBQ. I found my resources, and shaped my DBQ around what I had discovered. If I were to do this again, I would reverse my work flow. The topic would come first, and then I would find documents that fit with it. There would be more diversity in the sorts of documents that I included, rather than just using images.
While I do like my DBQ, and feel that it would get students to think about something that wouldn’t normally cross their minds, I am less pleased with the process that I went through to create my DBQ. My problems aren’t so much with my content as with my process. If anything, I became too attached to my content, and struggled to make changes because of that. ~ Emily Strocher AboutMe
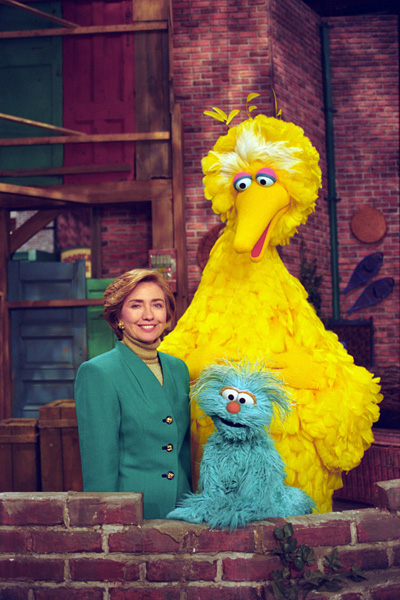
Image Credit: Photograph of First Lady Hillary Rodham Clinton Posing on the Big Bird Nest Set with Big Bird to Celebrate the 25th Season of Sesame Street , 10/14/1993
U.S. National Archives’ Local Identifier: P08630-13