The Pew Research Center has just released an update to its research series on political polarization in the American public. It provides engaging data visualizations and survey tools that are ideal for teachers and students of American government and politics. It’s also a great opportunity to explore news media literacy and critical thinking skills.
For more ideas on teaching politics join #sschat on Twitter on Monday Nov 3 at 7 PM (Eastern) for “Election ’14: Teaching Politics, Controversy and Civic Engagement”
I will be guest hosting #sschat with my social studies methods students @EdMethods.
The Pew political polarization research is based on a national survey of over 10,000 U.S. adults conducted by the Pew Research Center. There is an online version of that survey Where Do You Fit in the Political Typology? Teachers can create a “community group” and have their students sign in when taking the survey. You will be sent a link to your quiz page, which you should use when sharing the quiz with your community or group. After at least five members of the group have taken your quiz, you will be able to view the aggregate results on the group results page, which compares your group’s overall results with the general public’s.
Next, I would recommend reviewing the interactive graphs that demonstrate political polarization between 1994 and 2014. The new survey finds that as ideological consistency has become more common, it has become increasingly aligned with partisanship. Looking at 10 political values questions tracked since 1994, more Democrats now give uniformly liberal responses, and more Republicans give uniformly conservative responses than at any point in the last 20 years
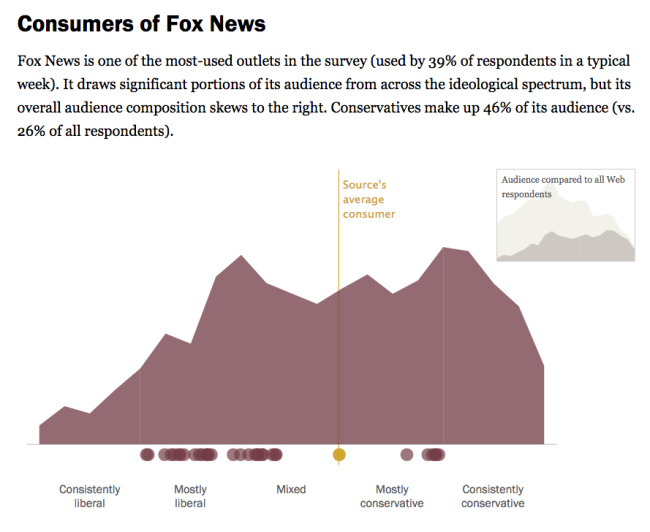
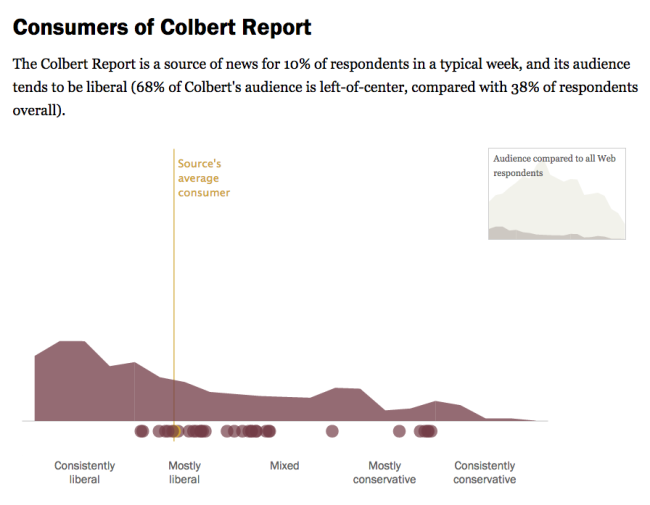
I would asks student to explore Political Polarization & Media Habits. When it comes to getting news about politics and government, liberals and conservatives inhabit different worlds. There is little overlap in the news sources they turn to and trust. And whether discussing politics online or with friends, they are more likely than others to interact with like-minded individuals, according to a new Pew Research Center study.
Students will enjoy exploring the sortable tables: Audience Profiles & Media Habits. There they can compare the audience profiles from diverse sources such as Wall Street Journal, Fox News, Colbert Report and the Glenn Beck Program.